
How Pomegranate Juice Can Wear Down Tooth Enamel
Jenn Hoskins
11th April, 2024
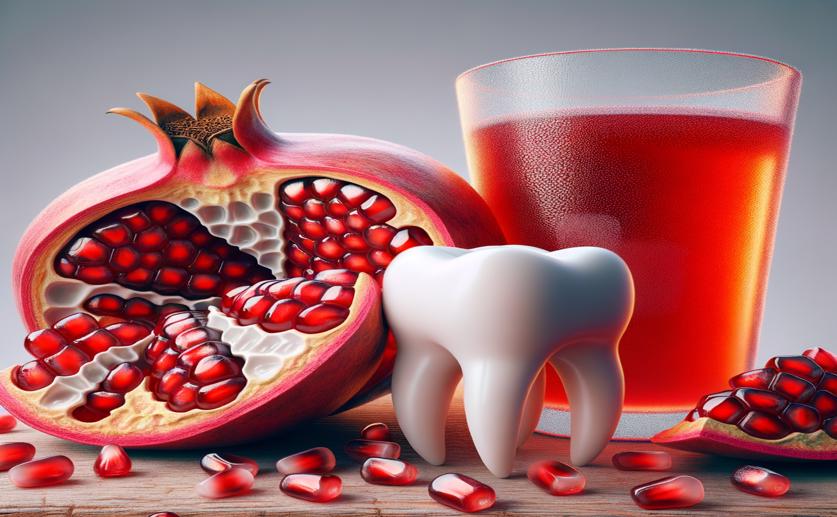
Image Source: Natural Science News, 2024
Key Findings
- Study from Xinjiang Medical University found pomegranate juice can erode tooth enamel
- Pomegranate juice caused larger fractures in enamel compared to the pitting by cola
- Despite its higher pH and calcium, pomegranate juice still harmed enamel significantly
References
Main Study
1) The erosive effect of pomegranate juice on enamel: An in vitro study.
Published 10th April, 2024
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0298404
Related Studies
2) Erosive tooth wear - a review on global prevalence and on its prevalence in risk groups.
3) Consensus report of the European Federation of Conservative Dentistry: erosive tooth wear--diagnosis and management.
4) Chapter 9: Acidic Beverages and Foods Associated with Dental Erosion and Erosive Tooth Wear.
5) The effects of pomegranate juice consumption on blood pressure and cardiovascular health.



 17th March, 2024 | Jenn Hoskins
17th March, 2024 | Jenn Hoskins